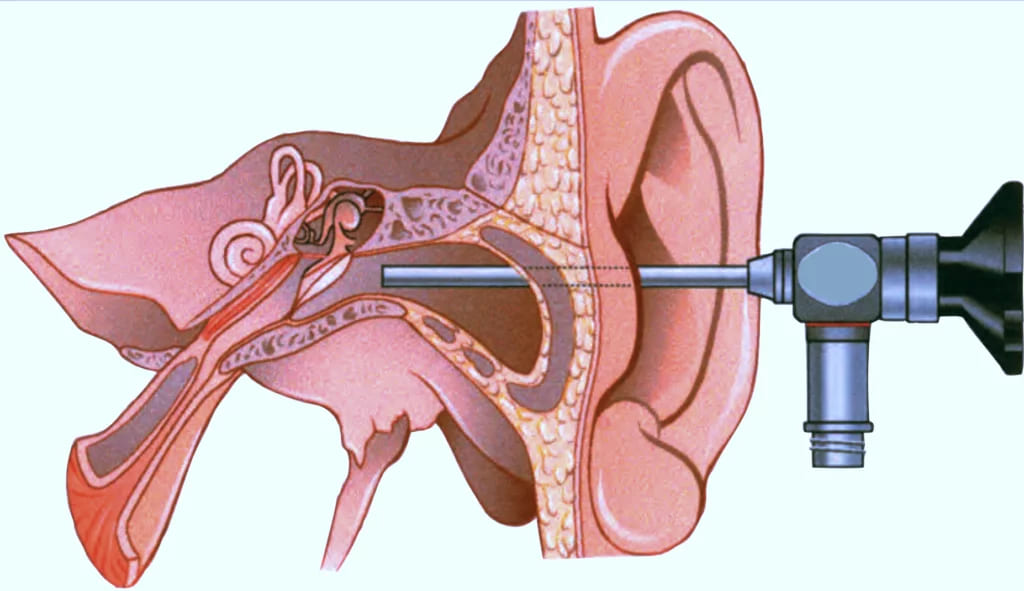
ADVANTAGES OF OTOENDOSCOPY
- It provides easy access to sinus tympani, facial recess, epitympanic sinus and protympanum, therefore helps in clearance of disease from these areas. These areas are anatomical blind spots for the operating microscope.
- Manoeuvrability.
- Proximity of image.
- Wide field of vision
- Angle of view
- There is reduced surgical morbidity.
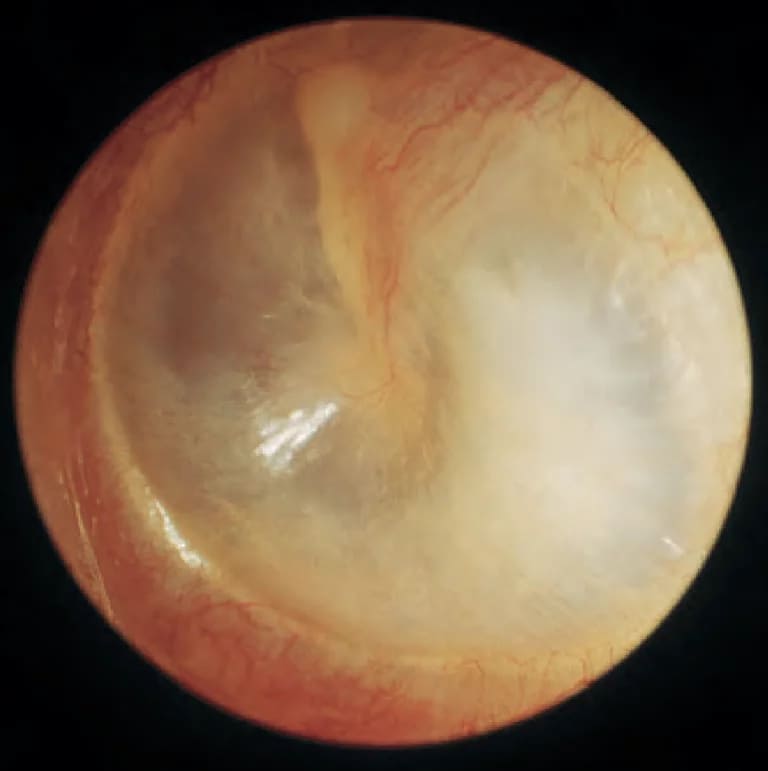
Endoscopic view of intact tympanic membrane
DISADVANTAGES OF OTOENDOSCOPE
- Only one hand free to operate.
- Peri-operative haemorrhage that leads to fogging and smearing of the endoscope tip.
- Limited movement by the extreme curvature of the external auditory canal (EAC).
- Risk of thermal injury to the middle ear
- Unsafe advancement during exploration can cause dislocation or fracture of ossicles.

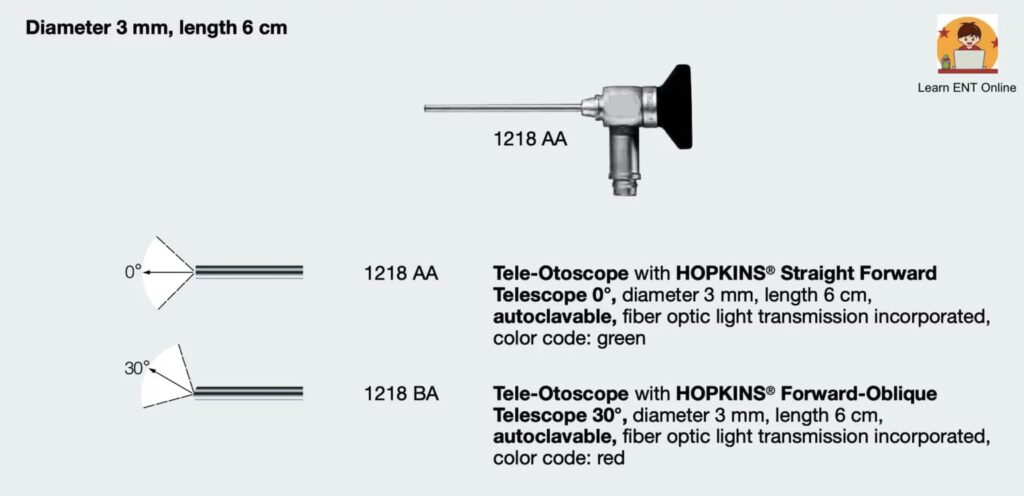
SPECIFICATIONS OF OTOENDOSCOPE
- Generally 3 mm and 4 mm diameter 0, 30 and 45 degree endoscopes are used.
- Rarely, 1.9 mm, 4.0 mm diameter and 70 degree endoscope are also used especially to pass through the posterior tympanotomy.
DIAGNOSTIC INDICATIONS
- Extent of retraction pockets and cholesteatoma. The diagnostic potential of the endoscope lies most commonly in the evaluation of retraction pockets and cholesteatoma, particularly in blind spots such as the sinus tympani, attic, protympanum and hypotympanum.
- Ossicular continuity through perforation. Evaluation of ossicular chain continuity may be under- taken endoscopically through an existing tympanic membrane perforation.
- Otoendoscopy through myringotomy. Middle ear endoscopy may also be carried out through a myringotomy for many indications such as unexplained conductive hearing loss, perilymphatic fistulas or occult cholesteatoma.
- Tympanoplasty/ ossiculoplasty surgery.
- Retraction pocket & cholesteatoma surgery.
- Minimally invasive second look canal wall up mastoid surgery.
- Newer applications include endoscopic stapedotomy, endoscopic cochlear implantation and total transcanal approaches to the inner ear.
Easy access to sinus tympani, facial recess, epitympanic sinus and protympanum, which were the anatomical blind spots for the operating microscope, therefore otoendoscopy helps in clearance of disease from these areas.
———— End of the chapter ————
Learning resources.
- Scott-Brown, Textbook of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery.
- Glasscock-Shambaugh, Textbook of Surgery of the Ear.
- Logan Turner, Textbook of Diseases of The Nose, Throat and Ear Head And Neck Surgery.
- Rob and smith, Textbook of Operative surgery.
- P L Dhingra, Textbook of Diseases of Ear, Nose and Throat.
- Hazarika P, Textbook of Ear Nose Throat And Head Neck Surgery Clinical Practical.
- Mohan Bansal, Textbook of Diseases of Ear, Nose and Throat Head and Neck surgery.
- Anirban Biswas, Textbook of Clinical Audio-vestibulometry.
Author:

Dr. Rahul Kumar Bagla
MS & Fellow Rhinoplasty & Facial Plastic Surgery.
Associate Professor & Head
GIMS, Greater Noida, India
msrahulbagla@gmail.com
Please read. Glomus Tumour. https://www.entlecture.com/glomus-tumour/
Follow our Facebook page: https://www.facebook.com/Dr.Rahul.Bagla.UCMS
Join our Facebook group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/628414274439500
