Electrocochleography (ECoG)
ECoG measures the electrical potentials generated specifically by the cochlea and the auditory nerve (CN VIII) in response to an auditory stimulus.
Potentials Measured: It records three main potentials:
- Cochlear Microphonics (CM): An alternating current (AC) potential generated primarily by the outer hair cells of the cochlea, which mirrors the waveform of the stimulus.
- Summating Potential (SP): A direct current (DC) potential reflecting the summed response of inner hair cells and possibly outer hair cells.
- Action Potential (AP): A compound action potential generated by the synchronized firing of many auditory nerve fibers (CN VIII).
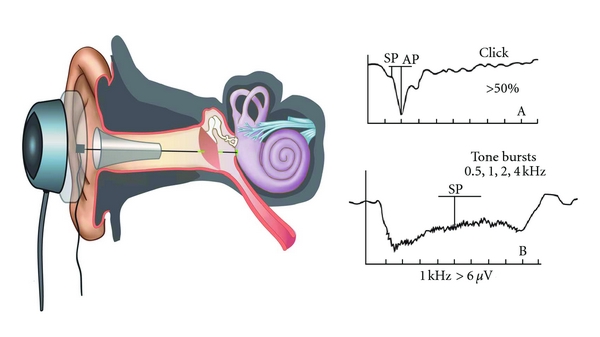
Procedure: ECoG is an objective test providing a reasonably accurate measurement of hearing thresholds between 1000 Hz and 8000 Hz. It typically requires inserting a thin, needle-like active recording electrode through the tympanic membrane and placing it onto the promontory or round window (transtympanic ECoG). Reference and ground electrodes are placed on the mastoid process and forehead, respectively. This procedure is usually done under sedation or local anesthesia due to its invasive nature. (Non-invasive extratympanic ECoG also exists, with electrodes in the ear canal, but provides smaller responses).
Uses of ECoG:
- Diagnosing Meniere’s Disease: A significantly enlarged SP/AP ratio (typically > 0.4 in transtympanic ECoG) is a highly characteristic finding in Meniere’s disease, indicative of endolymphatic hydrops. This is a key diagnostic marker.
- Detecting Hearing Thresholds in Difficult-to-Test Populations: It can estimate hearing thresholds (within 5-10 dB) in young infants, children, and uncooperative patients.
- Differentiating Cochlear from Eighth Nerve Lesions: By analyzing the characteristics of CM, SP, and AP, ECoG helps pinpoint the site of lesion within the inner ear or auditory nerve.
- Intraoperative Monitoring: Surgeons use ECoG to monitor the function of the cochlea and cochlear nerve during neurotological surgical procedures (e.g., acoustic neuroma removal, vestibular neurectomy) to preserve hearing.
———— End of the chapter ————
Download full PDF Link:
Electrocochleography (ECoG) Best Lecture Notes Dr Rahul Bagla ENT Textbook
Reference Textbooks.
- Scott-Brown, Textbook of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery.
- Glasscock-Shambaugh, Textbook of Surgery of the Ear.
- P L Dhingra, Textbook of Diseases of Ear, Nose and Throat.
- Hazarika P, Textbook of Ear Nose Throat And Head Neck Surgery Clinical Practical.
- Mohan Bansal, Textbook of Diseases of Ear, Nose and Throat Head and Neck Surgery
- Hans Behrbohm, Textbook of Ear, Nose, and Throat Diseases With Head and Neck Surgery.
- Salah Mansour, Middle Ear Diseases – Advances in Diagnosis and Management.
- Logan Turner, Textbook of Diseases of The Nose, Throat and Ear Head And Neck Surgery.
- Rob and smith, Textbook of Operative surgery.
- Anirban Biswas, Textbook of Clinical Audio-vestibulometry.
- Arnold, U. Ganzer, Textbook of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery.
Author:

Dr. Rahul Bagla
MBBS (MAMC, Delhi) MS ENT (UCMS, Delhi)
Fellow Rhinoplasty & Facial Plastic Surgery.
Renowned Teaching Faculty
Mail: msrahulbagla@gmail.com
India
———– Follow us on social media ————
- Follow our Facebook page: https://www.facebook.com/Dr.Rahul.Bagla.UCMS
- Follow our Instagram page: https://www.instagram.com/dr.rahulbagla/
- Subscribe to our Youtube channel: https://www.youtube.com/@Drrahulbagla
- Please read. Anatomy of External Ear. https://www.entlecture.com/anatomy-of-ear/
- Please read. Anatomy of Temporal Bone. https://www.entlecture.com/anatomy-of-temporal-bone/
- Please read. Stenger’s, Chimani Moos, Teal test. https://www.entlecture.com/special-tuning-fork-tests/
