A. Overview & Functions of the Ear (2 Points)
- Functions of the Ear – “HEAR” Mnemonic
- Hearing: Converts sound waves to nerve impulses.
- Equilibrium: The Vestibular system maintains balance.
- Alarm: Detects threatening sounds from the environment, acting as a warning system.
- Reception: Essential for speech and communication.
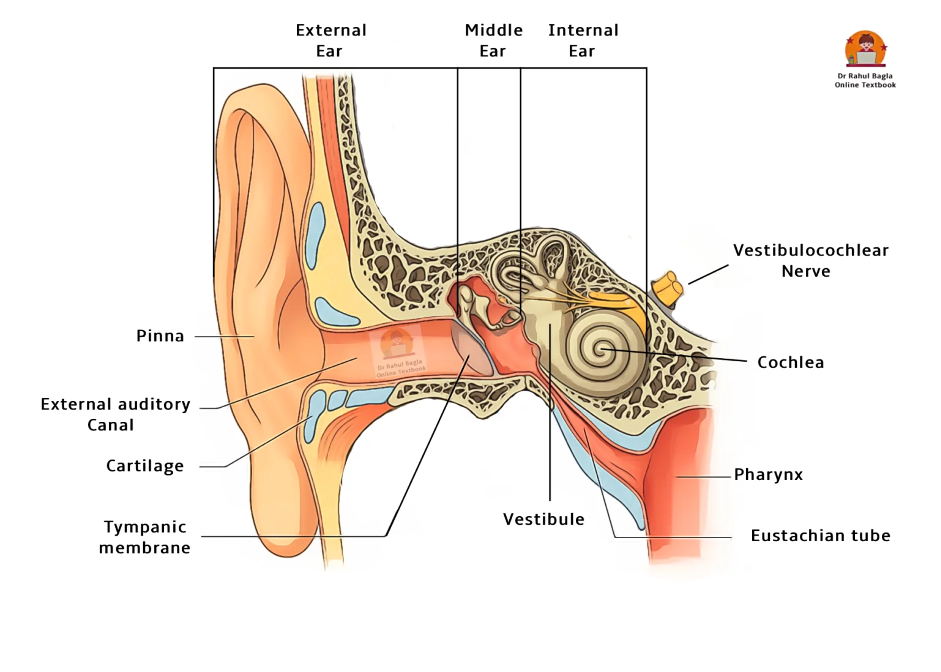
- Three Main Divisions of the Ear
- External Ear: Auricle (Pinna) + External Acoustic Canal + Tympanic Membrane.
- Middle Ear: Tympanic cavity + Ossicles + Eustachian tube.
- Internal Ear: Cochlea (hearing) + Vestibular apparatus (balance).
B. External Ear (Auricle/Pinna)
- Prominent Landmarks of the Pinna – “HAT CAG”
- Helix, Antihelix, Tragus, Concha, Antitragus, Groove (intertragic notch)
- Muscles, Blood & Nerve Supply
- Muscles: Extrinsic (3) & Intrinsic (6) – both by Facial Nerve (CN VII)
- Arterial supply: Posterior auricular (ECA), Anterior auricular (STA), Occipital (assist)
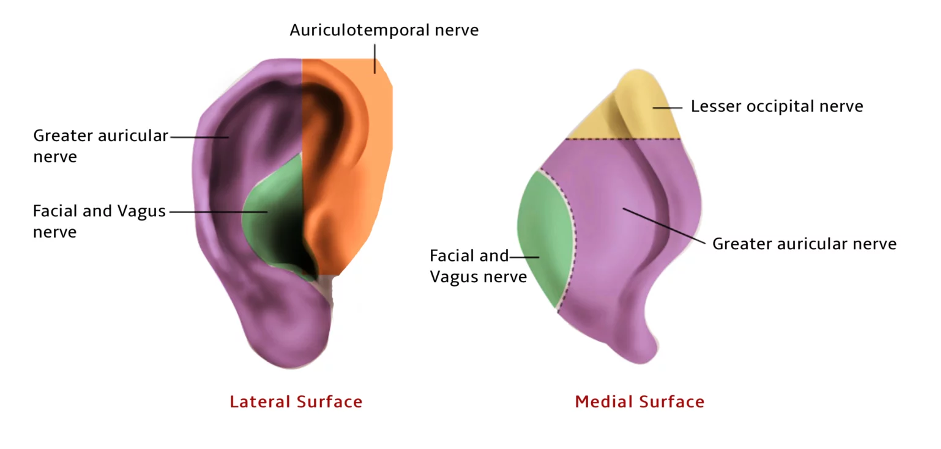
- Nerve supply:
- Greater auricular (C2–C3) – Posterior & medial pinna
- Auriculotemporal (V3) – Tragus, anterosuperior pinna
- Facial (VII), Vagus (X), Lesser occipital (C2) – Concha & postauricular region
- Lymphatic Drainage of the Pinna
- Medial Surface → Mastoid nodes
- Tragus/Upper Lateral → Preauricular nodes
- Rest of Pinna → Upper deep cervical nodes


C. External Auditory Canal (EAC)
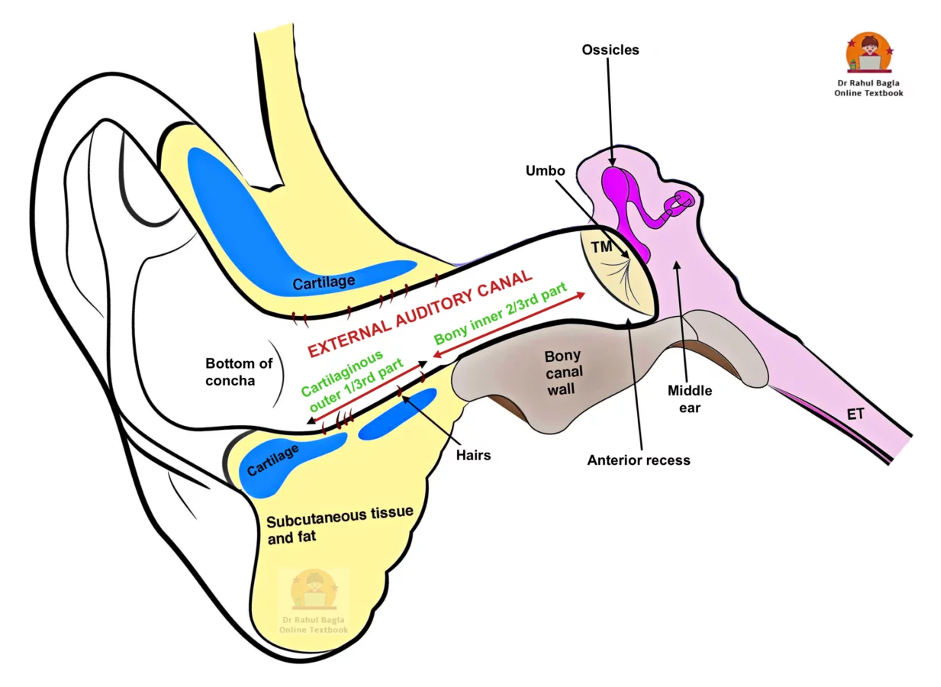
- Structure of EAC
- Cartilaginous outer 1/3 (8 mm) – Has hairs, ceruminous and pilosebaceous glands which produce earwax, furuncles are seen only in this part
- Bony inner 2/3 (16 mm) – Has isthmus (narrowing 5-6 mm lateral to the TM), making medial foreign body removal difficult. It also has an anterior recess that collects discharge but is hard to access; wax here or in the attic may signal cholesteatoma, and posterosuperior sagging can suggest mastoiditis.
- Shape of EAC: S-shaped; pull upward, backwards, and laterally for otoscopy
- Infection Pathways
- Fissure of Santorini – Present in cartilaginous EAC, increases flexibility but allows infections and neoplasms to spread to and from the parotid and temporomandibular regions.
- Foramen of Huschke – Present in bony EAC, acts the same as Fissure of Santorini
- Hitzelberger sign – Hypoesthesia of posterior meatal wall = Acoustic neuroma
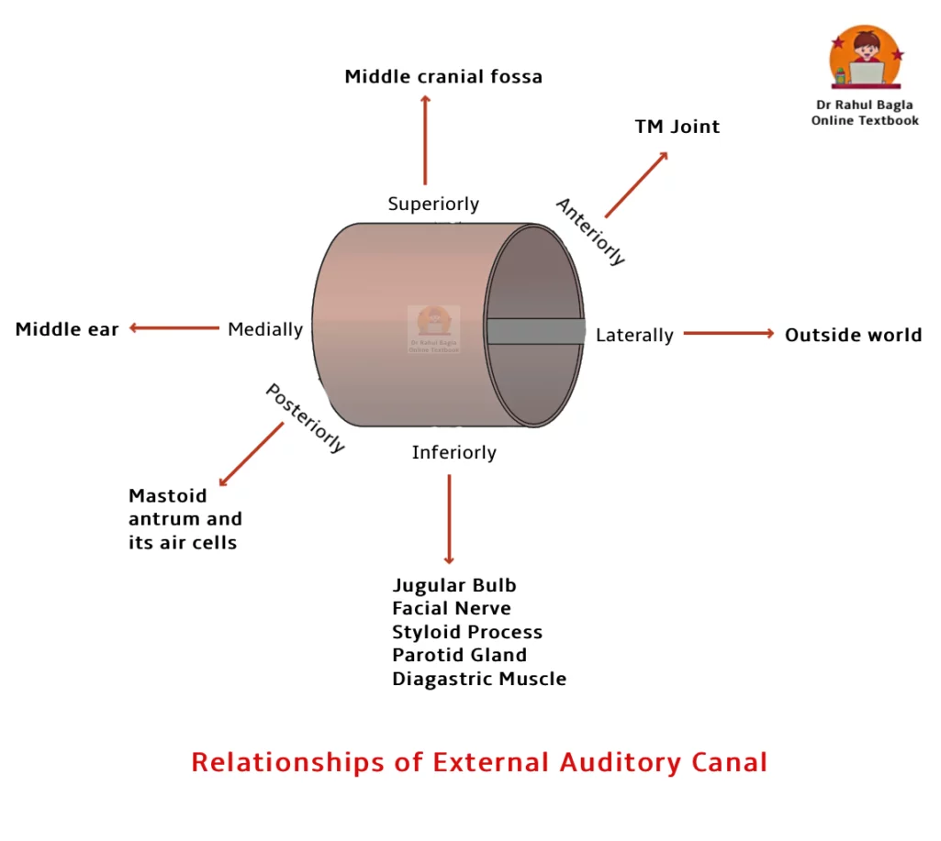
- Important Relationships of EAC
- Anterior: TMJ
- Posterior: Mastoid, facial nerve
- Superior: Middle cranial fossa
- Inferior: Parotid gland
- Medial: Tympanic membrane
- Lateral: Environment
- Nerve Supply of EAC
- Anterior & Superior: Auriculotemporal (V3)
- Posterior & Inferior: Arnold’s nerve (Vagus, CN X) – → Vasovagal reflex
- Posterior Wall: Facial nerve (CN VII)
D. Tympanic Membrane (Drumhead)
- Basic Features
- Size: 9–10 mm (height) × 8–9 mm (width)
- Thickness: ~0.1 mm
- Angle: 55° with the floor of the EAC
- Set obliquely: Posterosuperior is more lateral
- Colour: Pearly white
- Tympanic membrane has 3 Layers
- Outer Epithelial – continuous with skin
- Middle Fibrous – with radial & circular fibres
- Inner Mucosal – continuous with the middle ear
- Pars Tensa vs. Pars Flaccida
- Pars Tensa: Thick, has a fibrous layer, shows cone of light
- Pars Flaccida: Above malleus, lacks robust fibrous layer → cholesteatoma site
- Blood Supply
- Lateral surface: Auricular branch of maxillary artery
- Medial surface: Anterior tympanic, Stylomastoid branch (PAA), Middle meningeal
- Nerve Supply
- Lateral side:
- Anterior half: Auriculotemporal (V3)
- Posterior half: Auricular branch of Vagus (CN X) → Arnold’s Reflex
- Medial side: Jacobson’s nerve (Tympanic branch of Glossopharyngeal CN IX)
- Lateral side:
- Clinical Pearls for Otoscopy
- Normal TM: Shiny, pearly grey, visible cone of light
- Siegelization: Tests mobility using pneumatic otoscope
- Cholesteatoma suspicion: Wax/debris on pars flaccida or attic = red flag


———— End of the chapter ————
Reference Textbooks.
- Scott-Brown, Textbook of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery.
- Glasscock-Shambaugh, Textbook of Surgery of the Ear.
- P L Dhingra, Textbook of Diseases of Ear, Nose and Throat.
- Hazarika P, Textbook of Ear Nose Throat And Head Neck Surgery Clinical Practical.
- Mohan Bansal, Textbook of Diseases of Ear, Nose and Throat Head and Neck Surgery
- Hans Behrbohm, Textbook of Ear, Nose, and Throat Diseases With Head and Neck Surgery.
- Salah Mansour, Middle Ear Diseases – Advances in Diagnosis and Management.
- Logan Turner, Textbook of Diseases of The Nose, Throat and Ear Head And Neck Surgery.
- Rob and smith, Textbook of Operative surgery.
- Anirban Biswas, Textbook of Clinical Audio-vestibulometry.
- Arnold, U. Ganzer, Textbook of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery.
Author:

Dr. Rahul Bagla
MBBS (MAMC, Delhi) MS ENT (UCMS, Delhi)
Fellow Rhinoplasty & Facial Plastic Surgery.
Renowned Teaching Faculty
Mail: msrahulbagla@gmail.com
India
———– Follow us on social media ————
- Follow our Facebook page: https://www.facebook.com/Dr.Rahul.Bagla.UCMS
- Follow our Instagram page: https://www.instagram.com/dr.rahulbagla/
- Subscribe to our Youtube channel: https://www.youtube.com/@Drrahulbagla
- Please read. Anatomy of External Ear. https://www.entlecture.com/anatomy-of-ear/
- Please read. Anatomy of Temporal Bone. https://www.entlecture.com/anatomy-of-temporal-bone/
- Please read. Stenger’s, Chimani Moos, Teal test. https://www.entlecture.com/special-tuning-fork-tests/
Keywords: PPT Free Download, External ear nerve supply, Ear plugs, Ear lobe, Auricle or pinna, Anatomy of Ear, Muscles & Blood supply of pinna, Fissures of Santorini, Huschke.
